Popular Mike’s Hard xcritical Flavors, Ranked Worst To Best
13/03/2023Blockchain and the future of accountancy
19/04/20238 1: Compare and Contrast Variable and Absorption Costing Business LibreTexts
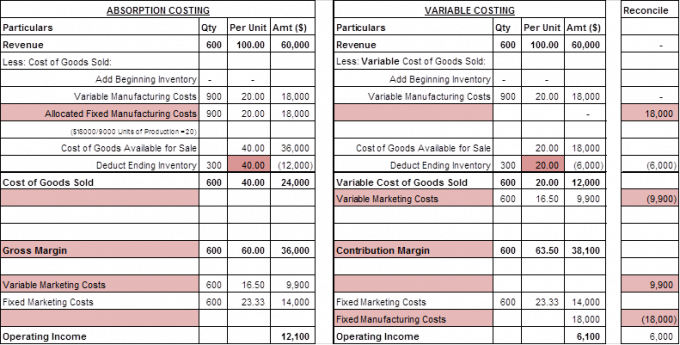
Cost of goods sold includes direct materials, direct labor, and variable and allocated fixed manufacturing overhead. From gross profit, variable and fixed selling, general, and administrative costs are subtracted to arrive at net income. It is the presentation that is typical of financial statements generated for general use by shareholders and other persons external to the daily operations of a business. One of the key differences between absorption costing and variable costing lies in the allocation of fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Absorption costing allocates these costs to units of production, regardless of whether they are sold or remain in inventory.
- Absorption costing also provides a more accurate accounting of net profitability, especially when a company doesn’t sell all of its products in the same accounting period in which they are manufactured.
- It may see an increase in gross profit after paying off the mortgage or finishing the depreciation schedule on a piece of manufacturing equipment.
- Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages, so it is crucial to understand their key differences.
Absorption and Variable Costing Problems and Solutions
This $20 per unit fixed cost would be allocated as a product cost for each unit sold, along with the $60 per unit variable costs. Contribution margin under variable costing is defined as sales revenue less variable product costs. This is an important metric as it represents the residual amount that is available to cover fixed costs and provide profit after the variable costs of production have been covered. Absorption costing and variable costing are two different methods of accounting for product costs.
Determining product vs. period costs
Absorption costing information may not always provide the best signals about how to price a product, reach conclusions about discontinuing a product, and so forth. Generally accepted accounting principles require use of absorption costing (also known as “full costing”) for external reporting. Under absorption costing, normal manufacturing costs are considered product costs and included in inventory. Management accounting is the process of tracking and managing a company’s product costs. Product costs are the expenses incurred in producing a good or service, and tracking and managing these costs is essential for ensuring that a company remains profitable.
Recap of Variable Costing Advantages
In management accounting, period costs are incurred in a specific period and can be directly linked to the revenues or activities of that period. For example, the salaries of employees who worked in a given month are period costs, as are the costs of materials used to produce products in that month. Absorption costing generally provides a more accurate picture of the true costs of production, while variable costing is typically more straightforward to implement. Businesses often use both methods to get the most accurate possible picture of their costs. Absorption costing is required for financial reporting under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Public companies in the United States must use absorption costing when preparing their financial statements.

Skewed Profit and Loss
Under absorption costing, they are allocated to units produced as product costs. Variable costing is a managerial accounting method that includes only variable production costs—direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead—in unit product costs. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs are treated as period costs and are deducted in full as an expense in the period incurred. Consequently, income before income taxes under variable costing is $600 less than under absorption costing because more costs are expensed during the period. With variable costing, all variable costs are subtracted from sales to arrive at the contribution margin. The variable product costs include all variable manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead).
Accounting Jobs of the Future: How Staffing Agencies Can Help Land Them
See the Strategic CFO forum on Absorption Cost Accounting that helps managers understand its uses to learn more. Even if a company chooses to use variable costing for in-house accounting purposes, it still has to calculate absorption costing to file taxes and issue other official reports. To determine product costs, you need to know the cost of each component that goes into making the product. The total cost of all the components that went into making the product multiplied by the number of units produced gives you the product cost. See the Strategic CFO forum on Absorption Cost Accounting that helps managers understand its uses to learn more.
Absorption costing includes all costs, including fixed costs, related to production, while variable costing only includes the variable costs directly incurred in production. Companies that use variable costing keep fixed-cost operating expenses separate from production costs. Variable costing is a method of accounting in which only variable costs are considered when making decisions.
Variable costing provides useful information for management decisions related to pricing, product mix optimization, and incremental analysis. Net income on the what can i deduct and what receipts should i keep for my taxes two reports can be different if units produced do not equal units sold. Let us assume that the total production units are 1000 and the cost card is as follows.
